Which is Better: EV Hub Motor or PMSM Motor for Electric Vehicles?
Introduction
The electric vehicle (EV) industry is evolving rapidly, and the choice of motor plays a critical role in determining vehicle performance, efficiency, and cost. Among the various motor technologies available, EV hub motors and Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSMs) are two of the most commonly used options.
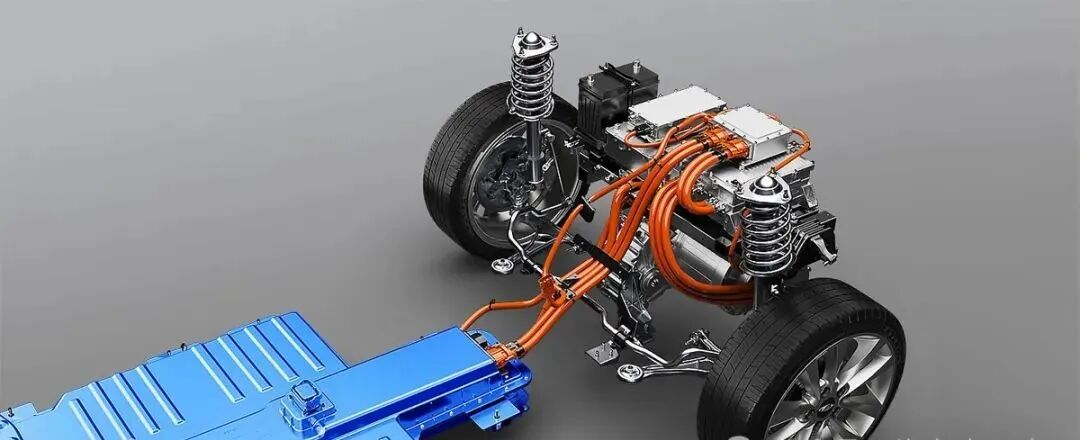
Both motor types have distinct characteristics that make them suitable for different applications. Hub motors are integrated directly into the wheel, offering a compact and simplified drivetrain, whereas PMSM motors are centrally located, delivering high efficiency and power output.
Understanding their differences is crucial for selecting the right motor for an EV. This article explores the fundamentals of EV hub motors and PMSM motors, highlighting their key differences, cost considerations, and best use cases to determine which is the better choice for various EV applications.
Understanding EV Hub Motors
What is an EV Hub Motor?
An EV hub motor is an electric motor that is built directly into the wheel hub of an electric vehicle. Unlike traditional EV motors, which require a drivetrain and transmission to transfer power to the wheels, hub motors deliver torque directly to the wheel. This makes them a popular choice for lightweight electric vehicles, such as e-bikes, e-scooters, and compact urban EVs.
How Do EV Hub Motors Work?
Hub motors function by placing the stator (stationary part) inside the wheel and having the rotor (moving part) rotate around it. When electricity is supplied, the magnetic field inside the motor interacts with the rotor, generating torque that directly spins the wheel. There are two main types of hub motors:
1.Direct Drive (Gearless) Hub Motors – These motors connect the rotor directly to the wheel, providing smooth operation with fewer moving parts but at the cost of increased weight.
2.Geared Hub Motors – These motors use a set of internal gears to amplify torque, offering better efficiency and torque at lower speeds, but with slightly more maintenance requirements.
Advantages of EV Hub Motors
- Simplified Design: Hub motors eliminate the need for a complex drivetrain, reducing vehicle weight and increasing space for batteries.
- Energy Efficiency at Low Speeds: Direct drive reduces power losses associated with gears and transmission.
- Independent Wheel Control: Offers precise control over each wheel, improving handling and stability.
- Lower Maintenance: Fewer moving parts mean fewer wear-and-tear issues.
- Regenerative Braking: Hub motors can efficiently convert kinetic energy into electrical energy during braking, improving efficiency.
Disadvantages of EV Hub Motors
- Higher Unsprung Mass: Since the motor is inside the wheel, the added weight can negatively impact suspension performance and ride quality.
- Limited Cooling Efficiency: Being enclosed within the wheel makes it harder to dissipate heat, potentially reducing efficiency and longevity.
- Lower Maximum Power Output: Hub motors typically have lower power density compared to centrally located motors like PMSMs.
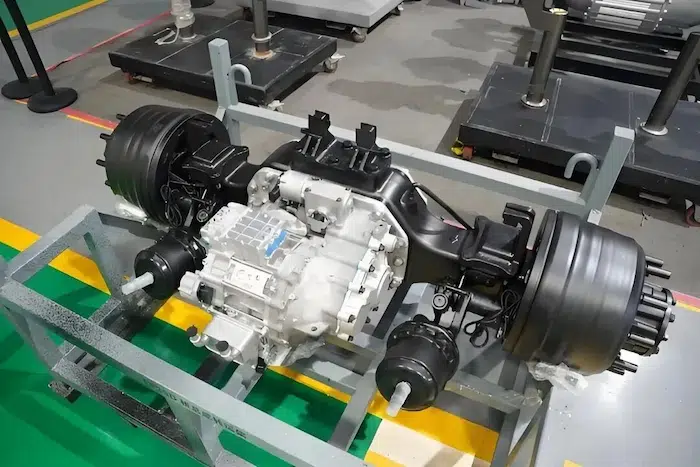
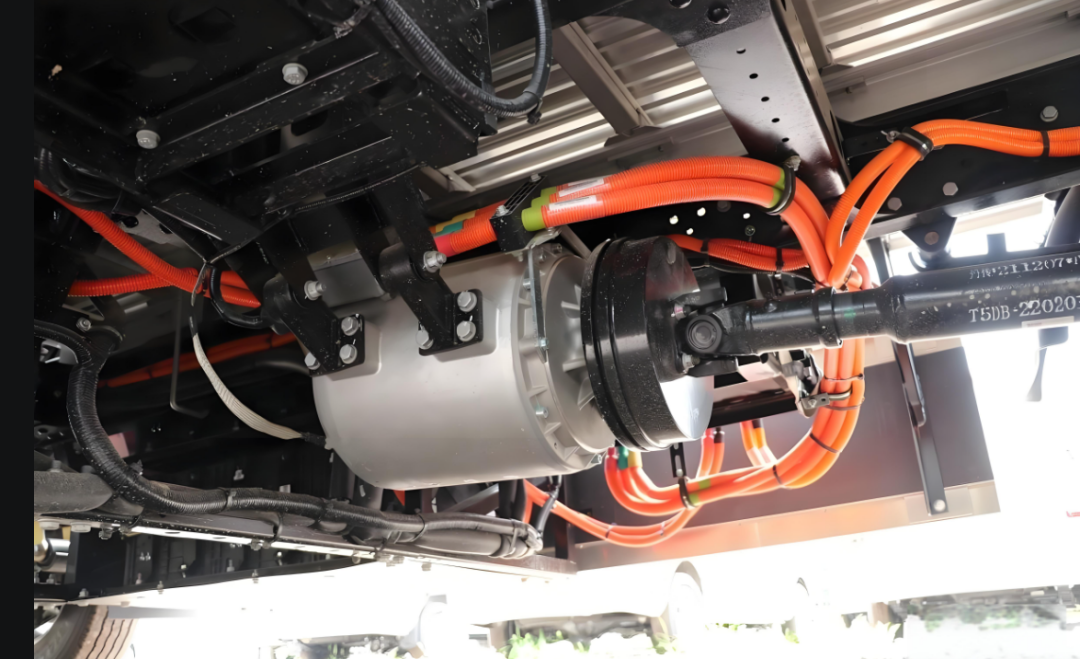
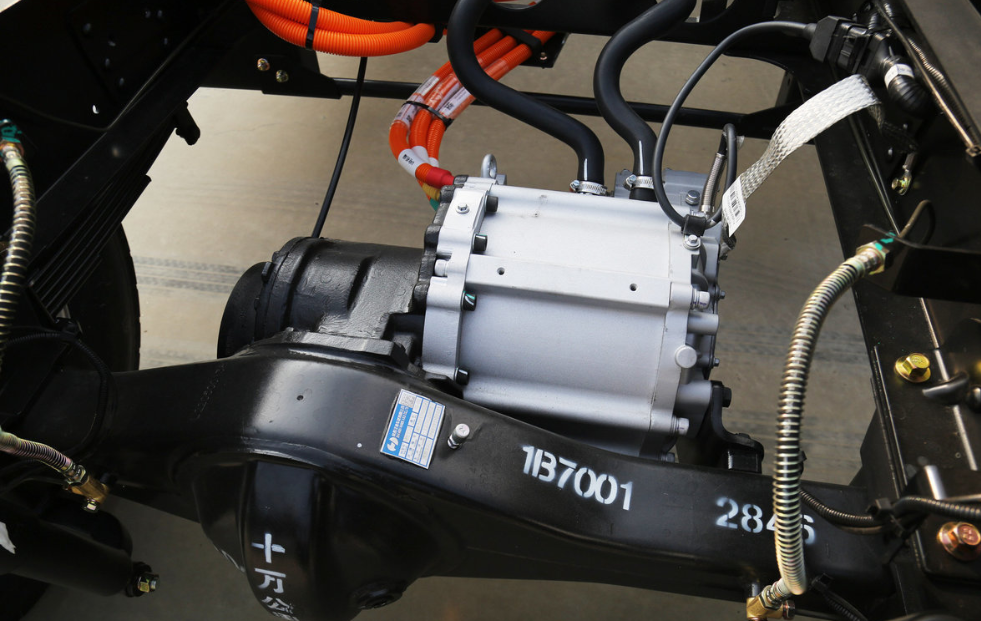
Understanding PMSM Motors
What is a PMSM Motor?
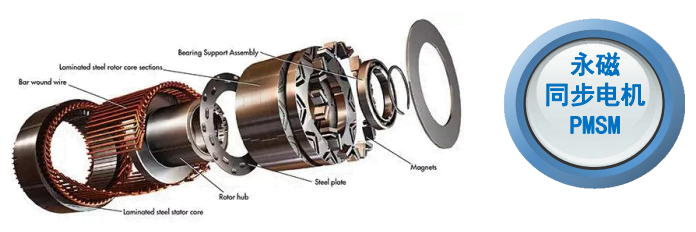
A Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) is a high-performance electric motor that uses permanent magnets embedded in the rotor to create a strong and efficient magnetic field. PMSMs are widely used in electric vehicles due to their high efficiency, superior torque output, and precise speed control.
How Do PMSM Motors Work?
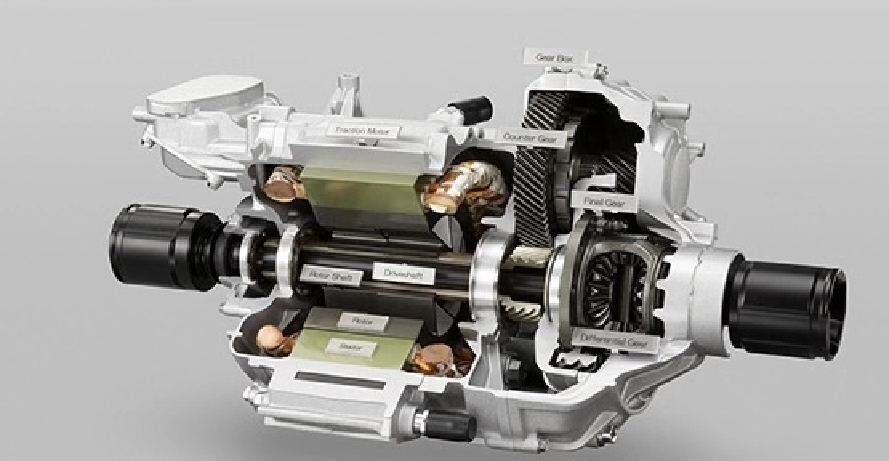
PMSMs operate using alternating current (AC) supplied by an inverter. The interaction between the stator's electromagnetic field and the permanent magnets in the rotor generates rotation, producing torque. The rotor moves synchronously with the stator's magnetic field, making these motors highly efficient at various speed ranges.
Advantages of PMSM Motors
- High Efficiency Across All Speeds: PMSMs maintain high efficiency even at high rotational speeds.
- Better Power Density: Offers more torque and power output relative to size compared to hub motors.
- Superior Cooling Capabilities: Centrally located placement allows better heat dissipation, enhancing longevity.
- Regenerative Braking Efficiency: PMSMs convert more energy back into the battery, increasing overall energy efficiency.
- Lower Unsprung Mass: Since PMSMs are not located in the wheels, they allow for better suspension performance and smoother rides.
Disadvantages of PMSM Motors
- Complex Control Systems: Requires sophisticated electronics and an inverter to manage performance effectively.
- Higher Initial Cost: Permanent magnets are expensive, increasing manufacturing costs.
- Requires a Transmission System: Unlike hub motors, PMSMs often need a gearbox or drive system, adding mechanical complexity.

Key Differences Between EV Hub Motors and PMSM Motors
|
Feature |
EV Hub Motors |
PMSM Motors |
|
Placement |
Inside the wheel |
Centrally located |
|
Power Transmission |
Direct drive |
Uses a driveshaft |
|
Efficiency |
Higher at low speeds |
Higher at high speeds |
|
Weight Distribution |
Increases unsprung mass |
Reduces wheel weight |
|
Maintenance |
Lower (fewer moving parts) |
Higher (due to transmission system) |
|
Cooling |
Challenging (inside the wheel) |
Easier (centralized cooling) |
|
Cost |
Generally lower |
Higher due to magnets and control systems |
Cost Considerations
Cost of EV Hub Motors:
- Lower Manufacturing Costs: Hub motors have fewer components, reducing production costs.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: Fewer moving parts mean fewer failures.
- Cheaper Integration: No need for a drivetrain or gearbox.
- Higher Initial Cost: Permanent magnets and sophisticated control systems make PMSMs more expensive.
- More Complex Assembly: Requires additional transmission components.
- Better Long-Term Performance: More efficient in high-performance EVs, making it cost-effective for premium applications.
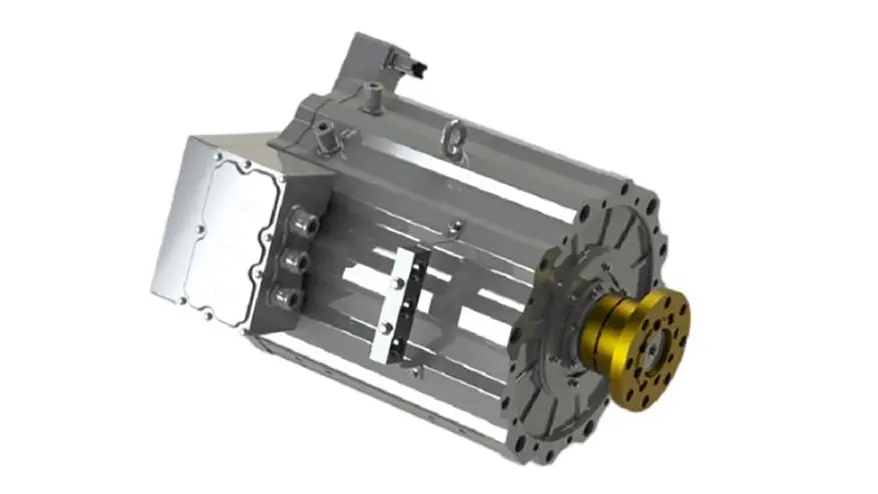

Best Use Cases for Each Motor Type
When to Use EV Hub Motors
1.Electric Scooters and E-Bikes: Ideal for lightweight personal mobility vehicles.
2.Small Urban Electric Vehicles: Best suited for city cars that don’t require high-speed efficiency.
3.Fleet Vehicles (Low-Speed Applications): Suitable for delivery scooters and bikes.
4.Autonomous Pods and Shuttle Services: Allows for precise control in self-driving vehicles.
When to Use PMSM Motors
1.Electric Cars and SUVs: Delivers better high-speed efficiency and overall performance.
2.Performance EVs: High-power applications benefit from superior torque and power density.
3.Commercial Vehicles and Buses: Ideal for larger EVs needing efficient cooling and variable-speed operation.
4.Racing EVs: PMSMs provide precise control and rapid acceleration.
Conclusion
Choosing between an EV hub motor and a PMSM motor depends on application and priorities.
EV hub motors are cost-effective, efficient at low speeds, and ideal for small electric vehicles, scooters, and autonomous shuttles.
PMSM motors are more expensive but provide better performance, efficiency at high speeds, and superior heat dissipation, making them ideal for electric cars, SUVs, and high-performance applications.
For personal electric mobility devices or urban commuting, EV hub motors are the best choice due to their simplicity and affordability. However, for full-sized electric vehicles and high-performance EVs, PMSM motors are the superior option.
By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each motor type, you can make an informed decision on which is better suited for your specific needs.
Read More: Xiaomi: Chinese Smartphone Giant Challenges Tesla in the EV Market